by dixie on Date unknown
ldif is Haskell library and tools for work with LDIF files. For the details about the LDIF please look LDIF on Wikipedia:
The LDAP Data Interchange Format (LDIF) is a standard plain text data
interchange format for representing LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access
Protocol) directory content and update requests. LDIF conveys
directory content as a set of records, one record for each object (or
entry). It represents update requests, such as Add, Modify, Delete,
and Rename, as a set of records, one record for each update request.
The parser from library is still not in 100% conformity with the LDIF related RFCs.
Use the HackageDB as usually.
$ cabal install HUnit
$ cabal install ldif
Please be aware that it is still ALPHA quality software.
Commands provided:
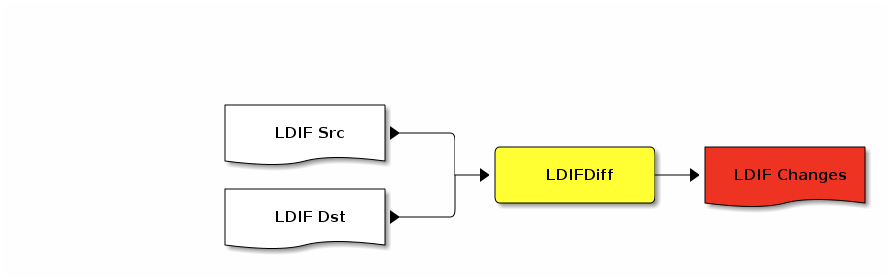
ldif2html - LDIF file pretty printing to the HTML filediffLDIF - Calculates delta between two LDIF filesldifmodify - Replays deltaldifparse - Ignore, only for parser debugging purposesCalculates delta LDIF based on two given content LDIF files.
If the change LDIF is applied into LDAP directory with state of content src.ldif the state will be changed to dst.ldif.
Delta LDIF contains LDAP operations like add, delete, modify. It is similar to the patch of the unix diff but on the LDIF files.
Usage:
diffLDIF: Create delta LDIF between Source LDIF and Target LDIF
diffldif [FLAG]
-? --help[=FORMAT] Show usage information (optional format)
-V --version Show version information
-v --verbose Higher verbosity
-q --quiet Lower verbosity
-s --srcFile=FILE Source LDIF File
-t --dstFile=FILE Target LDIF File
In pictures, there is process of Changes LDIF construction (diff): 
Process of applying changes LDIF into source LDIF (ldapmodify): 
See example LDIF files below.
Fist input file - filesrc.ldif
dn: cn=The Postmaster,dc=example,dc=com
objectClass: organizationalRole
cn: The Postmaster
oldAttr: attrValue1
oldAttr: attrValue2
dn: cn=The Postmaster Remove,dc=example,dc=com
objectClass: organizationalRole
cn: The Postmaster Remove
Second input file - filedst.ldif
dn: cn=The Postmaster,dc=example,dc=com
objectClass: organizationalRole
cn: The Postmaster
newAttribute: newValue
The command where files filedst.ldif and filesrc.ldif are involved:
$ diffLDIF -s filesrc.ldif -t filedst.ldif
Output of diffLDIF command - delta.ldif
dn: cn=The Postmaster,dc=example,dc=com
changetype: modify
delete: oldAttr
oldAttr: attrValue1
-
delete: oldAttr
oldAttr: attrValue2
-
add: newAttribute
newAttribute: newValue
dn: cn=The Postmaster Remove,dc=example,dc=com
changetype: delete
Replays the delta LDIF upon the content LDIF like the ldapmodify command.
If the diffLDIF is understood as the diff than the ldifmodify can be understood as the unix patch command.
Usage:
ldifmodify: Apply LDAP operations from LDIF to LDIF (like ldapmodify)
ldifmodify [FLAG] [LDIF Files for applying]
-? --help[=FORMAT] Show usage information (optional format)
-V --version Show version information
-v --verbose Higher verbosity
-q --quiet Lower verbosity
-f --baseFile=FILE Base LDIF File
-o --outFile=FILE Output LDIF File
Example is based on diffLDIF files
$ ldifmodify -f filesrc.ldif delta.ldif
The output of the ldifmodify example command above is filedst.ldif content.
The summary of the both diffLDIF and ldifmodify examples:
patch or diff between filesrc.ldif and filedst.ldif with name delta.ldifpatch file delta.ldif on filesrc.ldif and get the filedst.ldifThe above procedure is helpful when the delta.ldif is some kind of the patch applied on real LDAP directory, e.g. adding the users or updating of the structure.
It generates the brows-able LDIF as the HTML page.
Usage:
ldif2html <input.ldif> [<input2.ldif> <input3.ldif> ... <inputN.ldif> ] <output.html>